Getting Started
This API exposes attribution data generated by AIM in an easy-to-use and flexible GraphQL interface.
Authentication
To use the API, you will need to authenticate to the AIM platform with a JWT access token in the Authorization header of every request in the format Bearer {token}. To generate an access token you will first need to create an API application in the AIM Platform. This page also provides code samples for generating your access token, and a tool for generating a test token.
Once you have generated an access token, it is valid for 24 hours and you should store it for reuse rather than generating a new token for every request.
Using the API
GraphQL is an open source data query language originally created by Facebook. There are clients available for GraphQL in many programming languages but you can also simply make a pure HTTP POST request to the API. If you are not familiar with GraphQL, this is a good place to start.
Exploring / Testing the API
GraphQL Playground is provided as part of this API. The playground offers an intuitive user interface with intellisense and easy to use schema documentation to help you understand what data is available and experiment with queries. To make the playground work you must set a valid JWT token in the Authorization header within the headers section of the playground UI:
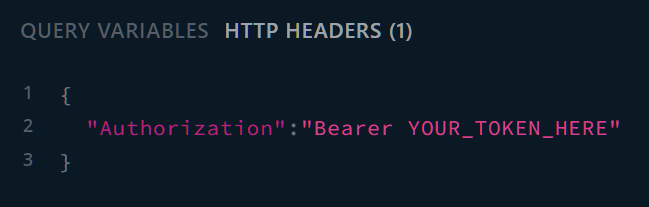
Schema Discovery
GraphQL APIs are self-documenting, and you can explore the API documentation in the playground.
- The Docs tab provides a searchable tree of available query fields with data types and descriptions of the purpose of each field and data type
- The Schema tab provides the raw GraphQL schema definition from which the documentation is built
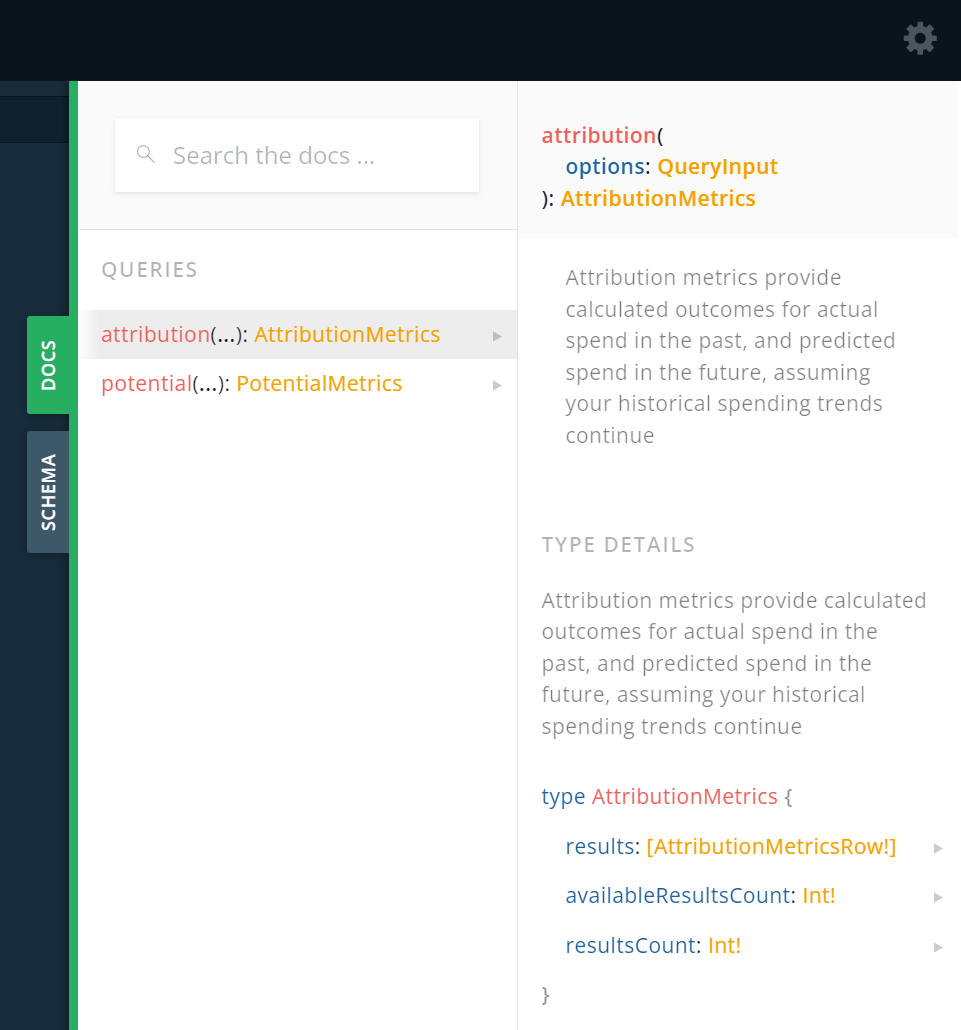
Schema
Unusually for a GraphQL API, this one has two distinct endpoints. This is because each app has it's own distinct set of available metrics and therefore it's own bespoke schema, so we provide an endpoint that contains an app ID which serves a schema-per-app, along with a higher level metadata schema on it's own endpoint to describe the available apps and other useful metadata.
It is possible to query a GraphQL API schema to discover what data is available with introspection queries.
Metadata Schema
This endpoint provides a list of available apps and other useful metadata. Use the documentation in the GraphQL Playground or introspection queries to discover exactly what data is available.
Metrics Schema
This endpoint provides attribution data for an app specified by the token :appId in the endpoint URL. Use the https://attribution.aimplatform.io/graphql endpoint to discover the available apps and associated app IDs. Use the documentation in the GraphQL Playground or introspection queries to discover exactly what data is available.
IMPORTANT: remember that the schema for this endpoint is app-specific. Although some properties such as networkId or date will be available for every app, there is no guarantee that the available metrics will be the same for every app, so you should always query the schema at runtime to discover which metrics are available before running your query to avoid errors.
Query Structure
Attribution / Potential
There are two top-level data collections available in the API: attribution, and potential:
- Attribution metrics provide AIM's calculated outcomes for your actual spend in the past, and predicted spend in the future, assuming your historical spending trends continue. Attribution metrics provide concrete, exact values for your metrics rather than a range of possible values, but you should always bear in mind that these values are probabilistic.
- Potential metrics predict the optimum possible outcomes for an optimal redistribution of your historic overall budget, which AIM will guide you towards. Potential outcomes are provided in the form of a min/max pair, representing the bounds within which AIM is confident that the actual value should fall should the spending advice be followed.
A typical query takes the following form (where attribution may be substituted for potential):
query {
attribution(options: { ...options }) {
results {
...key fields
...metric fields
}
}
}
The full range of options and available fields is documented in the GraphQL Playground, but for general context the following points should be understood:
- The options object enables sorting, filtering and pagination of the result set, as well as some control over the behaviour of record aggregation, such as with the periodicity option to control how dates are grouped
- Including one or more key fields (such as network_name or date) will cause the results to be broken down (disaggregated) by those keys. If you specify no key fields, a single result object will be returned representing the overall values for the whole app.
-
You must include at least one metric field. These are the actual values you are interested in seeing as the
output of your query. Remember, they are potentially different for each app.
-
You can modify a metric field with a transform function to adjust it's value based on the historical trend for that field. This is useful for moving averages. You can also specify the same metric field more than once with different modifiers, using GraphQL aliases. For example:
payments payments30DayEma: payments(transform: EXPONENTIAL_MOVING_AVERAGE, lookback: 30)
-
Help and Support
- GraphQL Getting Started Guide
- Kochava Support Website
- Send a support request to support@kochava.com
